What is Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC)/Cellulose Gum (E466) in Food and Uses?

What is Cellulose Gum | Properties | Uses | Safety | Side Effects | FAQs
Cellulose gum, or sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (sodium CMC), is a multi-functional ingredient that can be used as a thickener, binder, emulsifier and stabilizer in food with the European food additive number E466. Together with xanthan gum, they’re the most used and common thickener among others in food applications.
What Is Cellulose Gum?
Commonly we call CMC (used in food) is its salt, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose or sodium CMC instead of carboxymethyl cellulose itself.
Due to the poor water solubility of CMC, it is usually made into its sodium salt in order to be better use it.
Sodium CMC is a water-soluble cellulose ether obtained by chemical modification from natural cellulose such as cotton linter or wood pulp.
- Definition
- Structure
- What is it Used for?
- Is it Vegan?
- Is it Gluten Free?
- What is it Made of?
- How is it Made?
Definition
It is the partial sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of cellulose, the cellulose being obtained directly from strains of fibrous plant material.
EU changed the definition and synonyms of E466 Specification in 2013 to make it clear as follows (1):
| Present | Previous | |
| Heading | E 466 sodium carboxy methyl cellulose, cellulose gum | E 466 sodium carboxy methyl cellulose, carboxy methyl cellulose, cellulose gum |
| Synonyms | NaCMC; Sodium CMC | CMC; NaCMC; Sodium CMC |
Structure
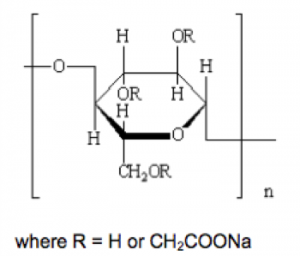
What is it Used for?
Cellulose gum is often used in foods and beverages to make foods thick and creamy to attract the appetite of customers. It thickens and stabilizes a lot of foods by retaining moisture, keeping oil and water phased ingredients don’t separate and produces a consistent texture and so on.
Is it Vegan?
Generally, it is vegan as it produced from cellulose, the plant-based fiber commonly from wood chips and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan.
Is it Gluten Free?
Yes, cellulose gum is typically gluten-free and people with celiacs can eat it. It is an ingredient commonly found in both gluten-free and gluten-containing food labels. It is produced from cellulose complying with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
What is it Made of?
It is composed of anhydroglucose unit with average 0.2-1.5 carboxymethyl groups (-CH2COOH) on it.
How is it made?
Generally, there are two steps in manufacturing process of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, alkalinization and etherification.
Step 1: Alkalinization
Disperse the raw material cellulose pulp in alkali solution (generally sodium hydroxide, 5–50%) to obtain alkali cellulose.
Cell-OH+NaOH →Cell·O-Na+ +H2O
Step 2: Etherification
Etherification of alkali cellulose with sodium monochloroacetate (up to 30%) in an alcohol-water medium. The mixture of alkali cellulose and reagent is heated (50–75°C) and stirred during the process.
- ClCH2COOH+NaOH→ClCH2COONa+H2O
- Cell·O-Na+ +ClCH2COO- →Cell-OCH2COO-Na
The DS of the sodium CMC can be controlled by the reaction conditions and use of organic solvents (such as isopropanol).
Specification
|
Other Names |
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium, CMC gum |
|
CAS Number |
9004-32-4 |
|
Chemical formula |
The polymers contain substituted anhydroglucose units with the following general formula: C6H7O2(OR1)(OR2)(OR3), where R1, R2, R3 each may be one of the following:
OR can be written as: [C6H7O2 (OH)x (OCH2COONa)y]n
|
|
Molecular Weight |
Higher than approximately 17 000 (degree of polymerisation approximately 100) |
Properties
Appearance
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless, granular or fibrous powder.
Degree of Substitution
Also called DS, it means the average number of hydroxyl groups substituted per glucopyranose unit. A complete substitution would provide a DS of 3.
According to the EU, food grade cellulose gum DS value is 0.2-1.5 carboxymethyl groups (-CH2COOH) per anhydroglucose unit. (2)
Solubility
In water
Yields a viscous colloidal solution with water. Cellulose gum has good solubility in water and absorbs water easily. It forms a colloidal solution when dissolved in cold or hot water.
The degree of substitution (DS) and viscosity are two main factors affecting its water solubility.
Generally, the viscosity is between 25 mPa.s and 50,000 mPa.s, It is only soluble in alkali when DS value < 0.3. It is water-soluble when the DS value more than 0.4 and it is easily be dissolved in water when DS approaches 0.7 and less water-soluble when DS above 1.
With the increasing of DS value, the transparency of its solution will be improved accordingly.
In organic solvents
Insoluble in organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, copper, chloroform and benzene.
Viscosity
Generally, the viscosity of its solution is related to the polymerization degree of cellulose (DP), the solution concentration, pH value, temperature, degree of substitution, and etc.
1. DP
Depends on the origin of the cellulolytic material.
2. Concentration
The viscosity increases with the going up of the solution concentration.
3. PH
Generally, the viscosity of the 1% sodium CMC solution reaches the highest level at pH range from 6.5 to 9.0. The viscosity does not change much in the PH value from 9.0-11.0.
The viscosity drops rapidly and begins to form CMC when PH<6. And the process will be complete at pH ≌2.5.
The viscosity will decrease at PH>9, initially the decreasing process is slow with the increasing of PH, but will accelerate when PH>11.5.
4. Temperature
The viscosity decreased with temperature increasing but it will rise when cool down. However, a permanent viscosity reduction will occur when the temperature rises to a certain level. The higher the degree of substitution, the smaller the viscosity is affected by temperature.
What are the Uses of Cellulose Gum?
Food
The food-grade of cellulose gum is primarily used as a thickener in our daily food. In the taste, it imparts the food a thickening and creamier characteristics, making it more appealing to consumers compared with that without it.
Generally, it functions as a thickening, suspending, emulsifying, stabilizing and film-forming agent in many foods such as in beverages, bakery, dairy, dessert products and meat products.
It can also replace some other thickeners, like guar gum, gelatin, agar, sodium alginate and pectin in some food applications. The application is various according to varieties of viscosities and mesh sizes.
Following are its main uses and functions:
- Beverages: stabilize the particles and improve the mouthfeel.
- Bakery: improve volume and texture, retain moisture and prolong shelf life.
- Dessert: retain fluids in hydrocolloid dressings, improve mouthfeel and reduce syneresis.
- Dairy: control ice crystal growth in ice cream, prevent syneresis and improve texture.
- Meat: water binding and improve yield.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, cellulose gum acts as a binding, emulsion stabilising, film forming, masking and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (3)
Toothpaste
Its role in toothpaste is to enable the liquid and solid raw material mix completely and provide the toothpaste a proper viscosity, brightness and smoothness in molding and flowing.
Others
Other uses such as in oil drilling, detergent, paper making, textile, mining, ceramic and so on.
Is Cellulose Gum Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practice in food for human consumption. (4)
It can be used for anticaking agent or free-flow agent, drying agent, emulsifier or emulsifier salt, formulation aid, humectant, stabilizer or thickener and texturizer in Cheeses, Food Dress, Art Sw Jelly & Fruit Jams and Froz Desserts. (5) (6)
EFSA
Sodium carboxy methyl cellulose (E466) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (7)
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
After the studies of short and long-term toxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity and other researches, in 2017, EFSA concluded that “there was no need for a numerical ADI and that there would be no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels for E466.” (8)
Authorised Uses And Use Levels
It is approved in the EU at quantum satis (QS), in almost all authorised food categories.
Its application is listed in Group I and separately by E 466. The following foods may contain with it (9):
- Desserts, snacks, edible ices, chewing gum
- Vegetable oil, breakfast cereals, food supplements
- Cream, milk products, dried fruit and vegetables
- Nut butters and nut spreads, cocoa and Chocolate products
- Bread and rolls, fine bakery wares, unripened and processed cheese
- Sauces, soups and broths, meat products
- Beverage
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “emulsifier, stabiliser, thickener and gelling agent.” (10)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 466. (11)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener. (12)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specified” set in 1989. (13)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether cellulose gum is bad for our health and what are the side effects. We understand that consumers prefer natural food and have concerns about modified cellulose used as ingredients in the foods we eat. It is generally considered safe but some people may be allergic or sensitive to it.
Allergy
An early report by The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) in 1997 that a 63-year-old woman was allergic to cellulose gum in barium sulfate suspension. Symptoms are pruritus and urticarial lesions on her abdomen, arms, and face, as well as mild periorbital edema. (14)
Frequently asked questions about Cellulose Gum
Is Cellulose Gum The Same As Cellulose?
Different, cellulose gum is the modified cellulose.
Is It Natural?
Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is not natural as mentioned above, it is synthesized by alkalinization and etherification although the raw material cellulose comes from natural.
Is It Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is It Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. The modified cellulose E466 has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Does it Contain Dairy?
No, it is not derived from and contain dairy.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the thickener – sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (sodium CMC)/cellulose gum (E466), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Properties about degree of substitution, solubility and viscosity
- Uses in food, cosmetic and pharmaceuticals
- Safety
- Possible side effects
- FAQs: it is vegan, halal, synthetic.
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



I am pregnant and obviously concerned with what I consume. I would like to know if soy milk containing the following ingredients have any health benefits for pregnancy:
Water
Ground Whole Soybeans (7%)
Minerals (E341)
Inulin
Acidity Regulator (E332)
Salt
Flavourings
Stabiliser (E460, E466)
Vitamins B2
Vitamin B12
Hi Simone,
Better turn to the soy milk manufacturer to ask if these ingredients are in their brand.
As far as I know, the ingredients used in food are generally safe, but very few people may be allergic to it.
The safety of ingredients with E number has been approved by the EFSA.
Vitamins are the supplement and you can see almost everywhere, maybe you have eaten folic acid in the early period of pregnancy. So please be assured their safety.
Inulin is a non-digestible carbohydrate, and the FDA intends to add it to the definition of dietary fiber. You can see here:https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/questions-and-answers-dietary-fiber
Great info about cmc/ e466 I desperately trying to find it’s nutritional information can you help? Preferably per 100g if possible
sorry, i have not have such information
Hi
For CMC, we know, it can be applied in various food, like ice cream, juice, fruit jam, dairy product, beer, lactic acid drinks, yogurt, syrups, bakery products, wine, sauces, seasoning, meat products, ect.
Actually, as you know, this chemical has a wide range of food use, but for different food, the used CMC is very different.
For example, CMC used for yogurt is quite different from CMC used for wine.
But, if we put the CMC, which is suitable for wine, into yogurt, the CMC can’t play its actual role at all.
Thus, what i actually need to know is the specific food, which CMC will be used in, not extensive use range as mentioned?
CMC has been found to cause microbiota dysbiosis and gut inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.006
Hi I want to use it for frozen veg burger patty,
Is it the best option or any other option is available??
And how to use it?
what concentration we used in food, is it 0.5% or 1%
I am allergic to E466. I had been getting allergy attacks from McDonalds frappe so I stopped drinking those. Symptoms were akin to hayfever, with unique throat irritation like bugs crawling in there. I recently consumed a Rico Grape Fruit Drink (made in Taiwan) and it gave a strong allergic reaction – symptoms beginning about 4 hours after consumption. This drink has only water, E466 and other ingredients which are all found in confectionery, so known to be safe. So after about 10 years I found the cause of my allergy problem.